4. Metamodeling
For CFD, FEM, and Look-up Tables.
Benefits of Local Model Network Architecture

- Distinction between rule premises (if…) and rule consequents (then…)
- Easy to interpret
- Well suited for high-dimensional input spaces
- Gained knowledge about premises and consequents can be used for DoE designs
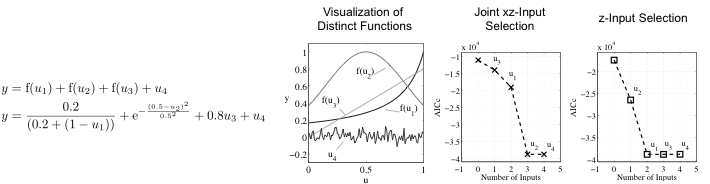
Artificial Example
AiF Project in cooperation with the Institute of Fluid- and Thermodynamics
(AiF: Arbeitsgemeinschaft industrieller Forschungsvereinigungen)
- Problem: New EU regulation requires higher degree of efficiency for ventilators
=> Most existing ventilators will be prohibited
=> New efficient dimensioning and optimization strategies required - Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD) models fulfill accuracy requirements, but:
- Many evaluations necessary for optimization
- Computationally very expensive
=> Economically unviable! - Approach to solving the problem:
- Metamodel: Model of the CFD model
- CFD model generates data set
- Local model network (LMN) is used
Local Model Network Advantages for the AiF Project Tasks
System Identification
- Automatic model complexity determination saves data for the training
- Akaike’s corrected information criterion (AICc) instead of validation data - Deterministic training procedure (no initialization required)
Design of Experiments
- Active learning strategy
- Structure of LMN is utilized to determine future CFD simulations - Exploitation of separation between linear and nonlinear effects
Optimization
- Local quadratic models can be used
- Very likely to find global optimum of the LMN
- M local models => M reasonable initialization points
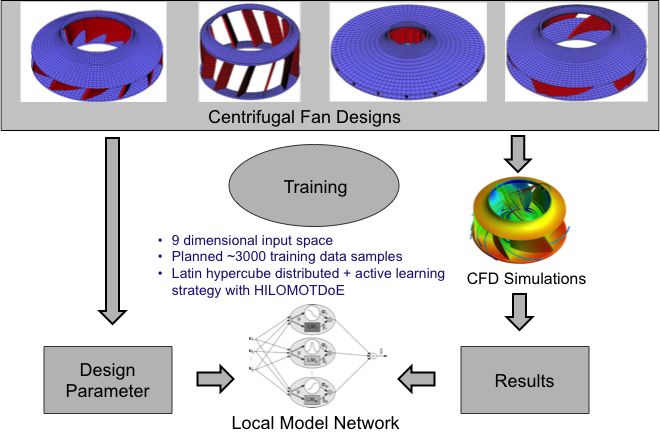
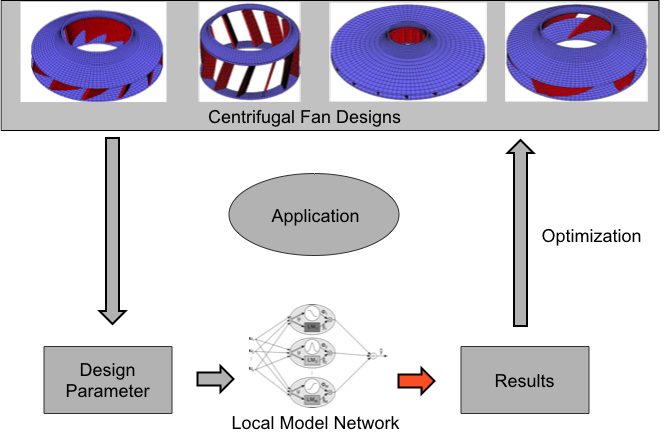
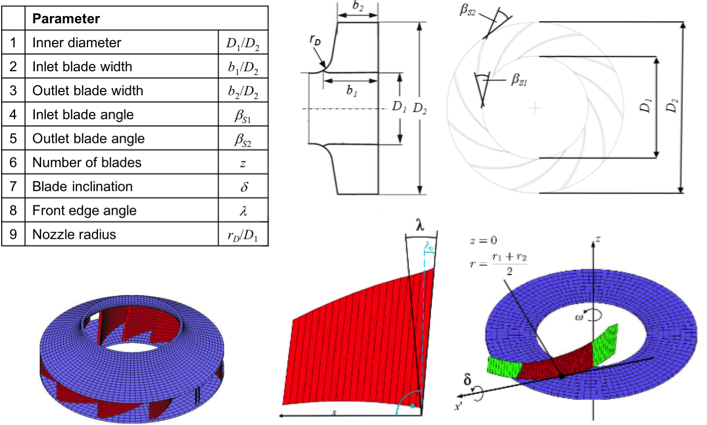
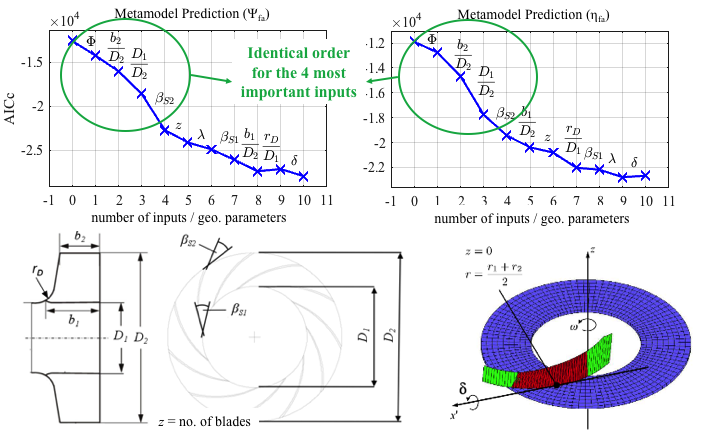
Construction of Centrifugal Fan
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations utilized (~4 hours per simulation)- Target values
- Pressure curve and efficiency curve - Design parameters
- Number of blades, inner and outer diameter, several angles, etc.
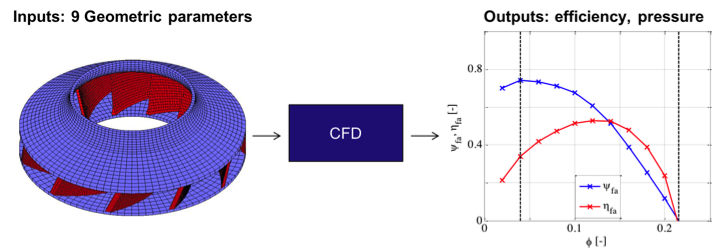
Two Metamodeling Approaches
1. Direct Metamodeling

- 10 inputs: Geometric parameters and volume flow.
- 2 outputs: Efficiency and pressure.
2. Indirect Metamodeling via Characteristic Curves
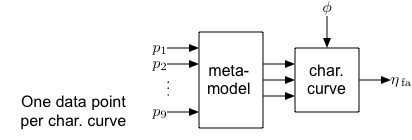
- 9 inputs: Geometric parameters.
- 3 or 4 outputs: Characteristic parameters of efficiency and pressure curves.
- 3 or 4 inputs: Characteristic parameters (metamodel outputs).
- 2 outputs: Efficiency and pressure.
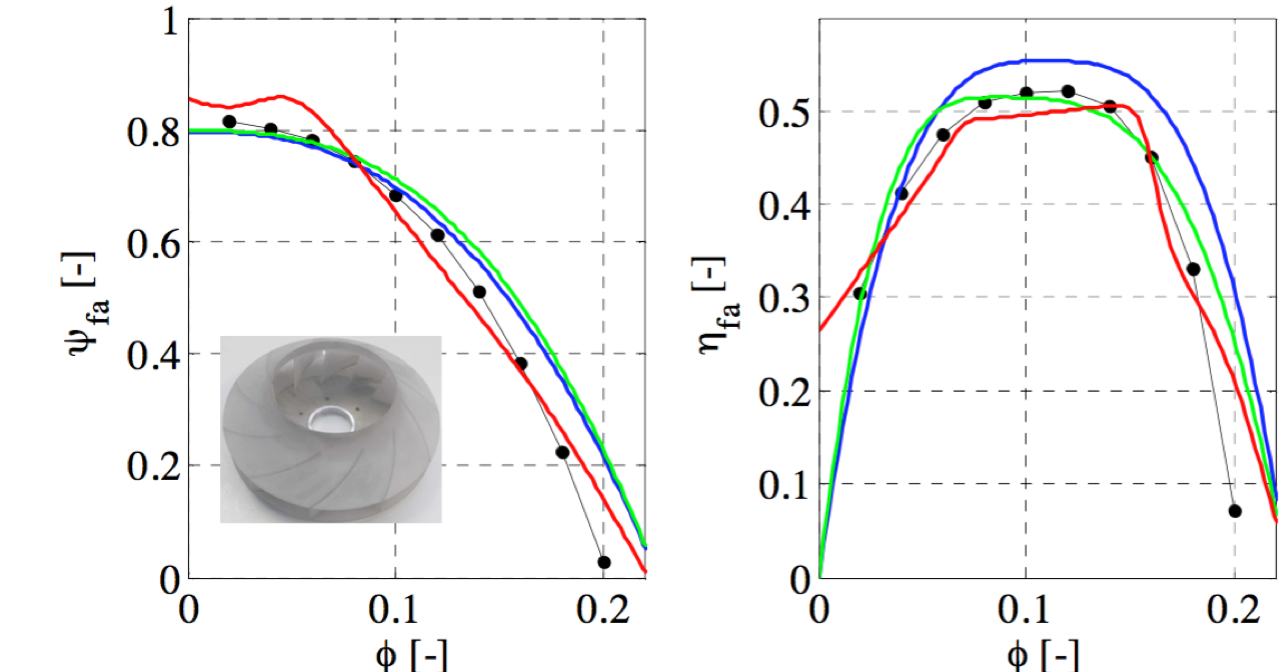
CFD (black line), Indirect (MIMO, blue line), Indirect (multiple MISO, green line), Direct (red line)
Next Chapter: 5. Nonlinear Dynamic Models Back to Overview
